Guide to Tax Form 1099MISC
This form will no longer report nonemployee compensation after 2020. We get it — let’s break down what this form means, why you received it, the filing requirements, and how to report it on your federal income tax return.
At a glance:
Form 1099-MISC reports miscellaneous compensation like rent, prizes, awards, and more.
- As of 2020, this form no longer reports nonemployee compensation.
- Payments on Form 1099-MISC need to be reported when filing your income tax return.
- What is the 1099-MISC form?
Form 1099-MISC, Miscellaneous Information, is one of many forms the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) uses to keep track of income that doesn’t come from a traditional employer. The IRS uses a variety of 1099 forms to report additional income. IRS Form 1099-MISC is an interesting one because it’s essentially a catch-all to report certain kinds of “miscellaneous compensation” that doesn’t quite fit into other 1099 categories.
Who gets a 1099-MISC form?
If you received a 1099-MISC form this tax season, it means you received miscellaneous payments above a certain amount. This can include rents, royalties, prizes, awards, and more — see the next section for examples of all the different types of payments reported on Form 1099-MISC.
Before 2020, Form 1099-MISC was also used to report nonemployee compensation for independent contractors, freelancers, and other self-employed individuals. However, the IRS now uses Form 1099-NEC to report this type of income instead of 1099-MISC.
You may also receive Form 1099-MISC if you were subject to backup withholding or if you purchased at least $5,000 of consumer products for resale outside a permanent retail establishment.
Example of Form 1099-MISC
Here is a 1099-MISC example so you can see what’s on this important tax form. As the payee you will receive Copy B. You’ll also see your contact information — you’ll find your recipient’s name, and TIN (typically, your Social Security number). Click on the payment types below for more information about what it means and how to report it:
Boxes 2 and 8:
These boxes report at least $10 in royalties (Box 2) or broker payments in lieu of dividends or tax-exempt interest (Box 8). Click on the payment type below to learn more about what it means, and how to report them:
Boxes 2, 8:
- These boxes report at least $100 in royalties (Box 2). They also report broker payments instead of dividends (Box 8) or tax-exempt interests (Box 8). Form 1099-MISC instructions
- Now that you have your 1099-MISC form in hand and know what it’s for, what should you do with it? Follow these steps to help streamline the tax filing process:
Check for accuracy:
Before you dive in, carefully review the information on your form. Double-check each box to ensure that the amounts are correct. If you notice an error, contact the issuer to get a corrected form ASAP.
- Determine where to report the income:
- The type of income you’ve received dictates where it goes on your tax return. TaxAct(r) makes this step easy — if you e-file with us, we’ll ask you detailed questions about your 1099-MISC income and pull all the necessary tax forms to report it accurately.Keep a copy for your records: Once you’ve filed your tax return, hang on to your 1099-MISC form and any related tax documents for at least three years. You’ll need them for your records in case the IRS has any follow-up questions.
- FAQs about Form 1099-MISCWhat are the 1099-MISC requirements?
The payer must file and send you a 1099-MISC form if you hit the reporting threshold for the type of payment you received (e.g., at least $600 in prizes or at least $10 in royalties). The payer must send the form by Jan. 31, meaning you should see it in your mailbox by mid-February.
As the recipient of Form 1099-MISC, you must report the payment(s) as income when filing your income tax return. Make sure to file by the due date (the filing deadline is typically April 15) to avoid any complications.
What’s the difference between 1099-MISC vs. 1099-NEC?
Prior to 2020, Form 1099-MISC was used to report nonemployee compensation of $600 or more to self-employed individuals. In 2020, the IRS introduced Form 1099 -NEC to track this compensation. It’s time to submit your 1099. Thankfully, this step is easy if you file with TaxAct — we strive to make the e-filing process smooth and straightforward for filers.
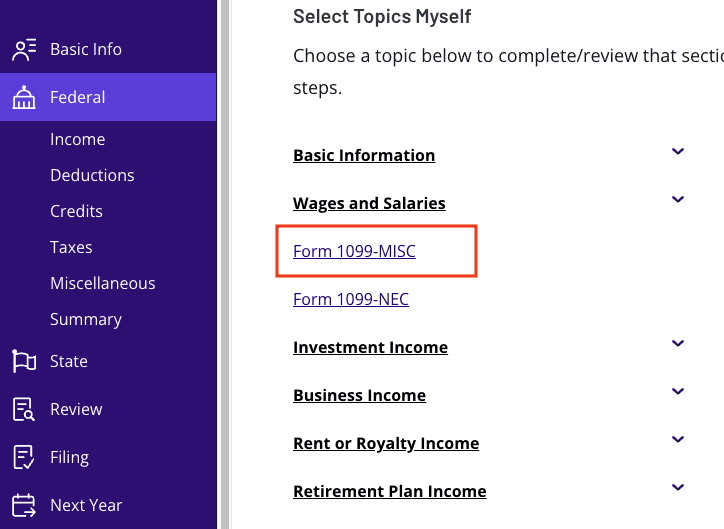
To report Form 1099-MISC with TaxAct:
From within your TaxAct return (
Online
or Desktop), click
Federal
- . (On smaller devices, click in the top left corner of your screen, then click Federal).Click Form 1099-MISC, as shown below:3. Click
- +Add form 1099-MISC, as shown below, to create a copy of the form. Or click Edit
if you want to edit an existing form. (Desktop program: click Review instead of Edit).4. Continue with the interview process to enter your information.Check out our FAQ page for additional tips on how to enter your 1099-MISC information in the TaxAct program.The bottom lineReceiving a 1099-MISC form doesn’t have to be confusing! This form is used to report miscellaneous compensation, such as rent, prizes, and awards. TaxAct will guide you through the process of reporting these payments on your tax return.